The history of Boeing Company | Timeline of aircraft & key events
Boeing is one of the world’s largest aircraft manufacturers. Founded on July 15, 1916, Boeing has a 106-year history of ups and downs, building and delivering more than 20,000 airplanes. As you would expect, the first planes they made were not nearly what we see in aviation today, so without a long introduction, let’s take a look at the beginnings of the company, the history of Boeing, and how it became the company it is today.
Boeing between 1910-1920

Boeing has been in this industry since the beginnings of aviation. In 1909, just six years after the Wright brothers’ first flight, William E. Boeing became absolutely fascinated with airplanes after seeing an aircraft exposition in Seattle. One year later, he bought a wooden boat manufacturing facility, the Heath Shipyard located at the mouth of the Duwamish River, which would later become his first airplane factory. His passion and dedication to airplanes led to the creation of his first airplane, the Boeing Model 1 or B&W Seaplane, and the founding on July 15, 1916, of the “Pacific Aero Products Co”, which would become the “Boeing Airplane Company” a year later, in April 1917.
The first airplanes built by Boeing
The first airplanes built by Boeing, from 1916 to 1920, were mostly seaplanes. Starting with the first airplane built entirely by the company, the Boeing Model 1 or B&W seaplane, to 1920 when the company built the Boeing Model 8, an airplane built in a single unit for flight tests.

On June 15th, 1916, Boeing Model 1 (B&W) made its first flight. This aircraft was a seaplane biplane, single-engine aircraft built in only two units. It was bought by the New Zealand Flying School, making it Boeing’s first international sale. In 1919 this plane began to be used for express and airmail deliveries in New Zealand. Today the original airplane no longer exists, but a replica can be seen at the Museum of Flight in Seattle.
The first financial succes for Boeing
The second plane built by Boeing also turned out to be the company’s first financial success. Boeing Model 2, also called Boeing Model C, was a 2-seat seaplane biplane built for training purposes. It had its first flight in November 1916 and was the first important airplane for the Boeing Company.

In 1917, World War I was in full swing and the US Navy needed planes for training. Boeing saw this as an opportunity and sent two Model C planes to the Pensacola Naval Base with pilot Herb Munter and Boeing factory superintendent Claude Berlin. At the time the aircraft could not fly such a long distance so the planes were sent disassembled by train to be assembled at the naval base. After testing and despite the bad weather conditions, the Boeing Model C proved to be better than anything the Navy had seen. That led to a contract for Boeing worth $575,000 ( which would be worth approximately $13,819,927 in 2022) for 50 Model C aircraft. After this first success, all of the company’s operations moved to Boeing’s first airplane production facility, Boeing Plant 1 in Seattle, Washington.

In November of that year, the Boeing XP-9 had its maiden flight, which was the first monoplane fighter made by Boeing. Only one such aircraft was built, but its features and design led to the creation of the famous P-26 Peashooter 2 years later. Flying 27 mph faster than biplane fighters, it was much more agile, resulting in a total of 151 Peashooters being built.
Boeing after World War I
After the First World War ended in November 1918, there was no longer a need for military aircraft and the entire civilian aviation market was flooded with ex-military planes. Boeing found itself in a situation where it couldn’t sell any planes, and in order to survive that period, the small airplane manufacturing company started building dressers, counters, furniture and flat-bottomed boats called sea sleds.
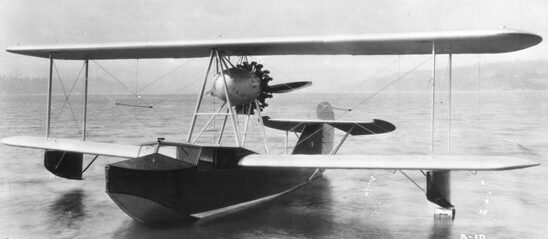
The Boeing Model 6, also called the B-1 Seaplane, made its first flight in December 1919. It was the first commercial airplane made by Boeing, a flying boat created for the purpose of carrying mail or cargo. It was built in a single unit and carried air mail for 8 years between 1919 and 1927.
Boeing in 1920s
In the early 1920s the Boeing Company, then called the “Boeing Airplane Company” was struggling to survive through the post-World War I surplus of airplanes. A major event of the year 1920 for Boeing was the flight of the Boeing Model 8, also called the BB-L6, the first airplane to fly over Mount Rainier.

At that time the company was kept afloat by orders from the Army Air Service to build 200 Thomas-Morse MB-3A fighters, which was also the first fighter plane built by Boeing, and to upgrade 298 British fighters.
Boeing’s first competition for a contract

In 1923, Boeing and Curtiss began the race to build the best pursuit fighter for the United States Army Air Service. The first to receive a contract for its design was Curtiss, but 6 months later, after Boeing had completed the Boeing Model 15 (PW-9) it too received a contract with the Army Air Service. The Model 15 and its derivatives propelled Boeing to the top spot for fighter jet sales for the next decade.
Boeing’s first airline

In 1925, the Boeing Model 40 had its first flight. This was the first aircraft built by Boeing that could carry passengers. It was a single-engine biplane that had the capacity to carry 2 passengers and 1,200 lb of mail or cargo.
In 1927, the Boeing Model 40A, an improved version of the Model 40 won the U.S. Post Office contract to deliver mail between San Francisco, California and Chicago, Illinois. Thus for the new airline Boeing Air Transport was formed, which had its first inaugural airmail delivery flight on July 1, 1927. In the first year alone, Boeing Air Transport carried 837,211 pounds of mail, 149,068 pounds of express packages, and 1,863 passengers.
Boeing’s first passenger aircraft
By 1928 Boeing had 800 employees and was recognized as one of the largest airplane manufacturers in the country.

On July 27, 1929, the Boeing Model 80, the first passenger airplane built by Boeing, made its maiden flight. It had a capacity of 12 passengers, was a 3-engine biplane and served the Boeing Air Transport airline. A larger version of this model was built later, the Boeing Model 80A with a capacity of 18 passengers.
In October 1928, to cover airline and airplane manufacturer operations, Boeing Airplane and Transport Corp. is formed. Just a few months later, it changes its name to United Aircraft and Transportation Corp. which by the end of 1929 expands its operations and buys multiple companies including Pratt & Whitney Aircraft Co.
Boeing in 1930s
In the 1930s Boeing became the leading manufacturer of all-metal airplanes. The company created planes that became benchmarks for passenger transportation, created new routes and major changes were made at the corporate level in the company.
The first monoplanes built by Boeing

On May 6, 1930, Boeing’s Model 200, the Monomail made its first flight. It was Boeing’s first commercial monoplane, a revolutionary aircraft for its time. It had retractable landing gear and laid the foundation for the production of monoplane aircraft. In total two units of this model were built, the Model 200 used to carry mail ,and the Model 221 used to carry mail and passengers. Both models were later converted to 8-man passenger planes to serve United Airlines, part of United Aircraft and Transportation Corp. one of Boeing’s many facets.

In November of that year, the Boeing XP-9 had its maiden flight, which was the first monoplane fighter made by Boeing. Only one such aircraft was built, but its features and design led to the creation of the famous P-26 Peashooter 2 years later. Flying 27 mph faster than biplane fighters, it was much more agile, resulting in a total of 151 Peashooters being built.
Boeing’s first modern passenger aircraft-Model 247

The Boeing Model 247 was one of the first modern passenger planes of its time. It entered service in May 1933 and was capable of carrying 10 passengers and 3 crew members. The Model 247 had two engines and was able to fly with only one engine in case the other one failed.
To give United Airlines an advantage over its competitors, Boeing decides not to offer the Model 247 to other airlines until after the first 60 planes are delivered to United. This led to major competition for Boeing and the creation of the DC-1 aircraft designed by Douglas Commercial which turned out to be larger and faster than Boeing Model 247.
Boeing after the Air Mail Act of 1934
In 1934 the Air Mail Act was passed, which prevented airline companies that carried mail and those that manufactured airplanes from being under the same parent company. This resulted in the division of Boeing’s United Aircraft and Transport Corp. into three companies: United Air Lines – responsible for transportation, United Aircraft (later called United Technologies) – responsible for production in the eastern United States, and Boeing Airplane Co. – responsible for production in the western United States. Disillusioned by the break-up, William Boeing sells all his shares and leaves Boeing to raise horses in late 1934.
Boeing in the period before World War II

Boeing’s new president Clairmont “Claire†L. believed the future for Boeing would lie in large airplanes, both bomber and passenger planes. Thus, the largest airplane in the United States at the time, the Boeing XB-15 was designed and took its first flight in 1937. It was a bomber with a wingspan of 149 ft and had 4 engines, but it proved to be a slow plane and only one prototype was built.
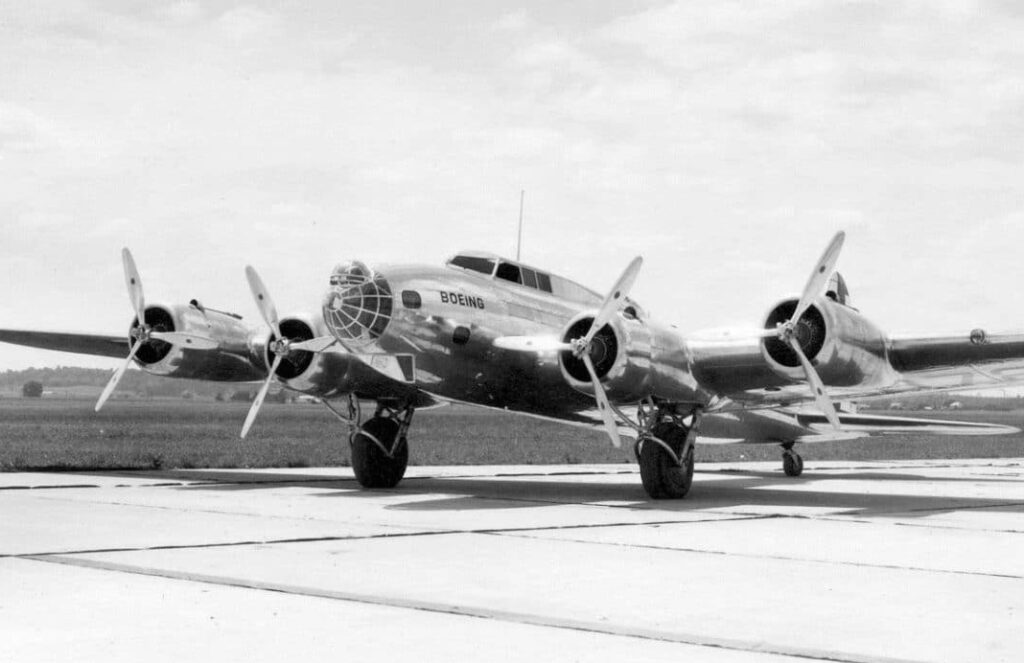

At the same time the Boeing XB-17 (Model 299) was built, a 4-engine heavy bomber that was destroyed in an accident only 3 months after its first flight. However this was a prototype for the B-17 Flying Fortress which was a real success for Boeing in WWII.

The characteristics of these huge planes led to the creation of the Boeing Model 314 Clipper. It made its first flight in 1938 and was the largest and most luxurious passenger plane of its time. Its four engines were capable of carrying 90 passengers, 11 crew members and cargo over long distances. In 1939, the first scheduled transatlantic airline was inaugurated between the United States and the UK using a Model 314 Clipper. After a period, Pan Am Airlines flew this aircraft on routes all over the world until its retirement in 1948.

The B-17 Flying Fortress aircraft led to the creation of the Boeing Model 307 Stratoliner, the world’s first pressurized cabin airliner. It made its first flight in 1940 and together with the Model 314 Clipper took passenger transport to an unprecedented level at the time. Thus air travel became extremely popular and in 1940 alone, a year when the world was at war, a total of 2.2 million people traveled by air.
Boeing in 1940s
The 1940s for Boeing were marked by the military aircraft that proved essential to the United States in World War II and the beginnings of the jet age.
The Boeing Company in World War II


During the Second World War, US aircraft manufacturers worked together to produce as many planes as possible. Boeing delivered a huge number of B-17 Flying Fortress and B-29 Superfortress bomber planes. Approximately 13,000 B-17s were produced across the country, of which 7,000 were produced by Boeing.
Just 2 years after its first flight, the Boeing B-29 Superfortress was introduced in May 1944. By the end of production, nearly 4000 B-29s had been produced. It proved to be the most important aircraft for the United States in World War II as it carried the atomic bombs that were used on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945. The B-29 Superfortress is also the only aircraft from which an atomic bomb was dropped in wartime.
The planes built at that time were mostly built by women whose men were at war. They increased production level from 60 planes a month in 1942 to 350 planes a month in 1944. Their work in aircraft factories was vital, which is why, to avoid risking an aerial bombing of Boeing’s Seattle plant, the tops of the Boeing Plant 2 buildings were covered with camouflage.
Boeing Company development after World War II

After World War II ended, all orders for military bomber aircraft were withdrawn. Boeing was forced to close factories and about 70,000 people lost their jobs, but the company has promised to rehire once they receive orders for their new C-97 Stratocruiser passenger plane. The Stratocruiser (Model 377) was a large airliner with 4 engines, a pressurized cabin, and two passenger decks. It was derived from the C-97 Stratofrighter, a military transport aircraft and was first introduced in 1949 with Pan Am Airways. Despite these extraordinary features for a passenger aircraft of that time, orders for the Model 377 (C-97) Stratocruiser did not live up to expectations. This marked the end of an era for the company, and the C-97 is the last propeller-driven aircraft built by Boeing.


The era of jet engines has begun and the first jet aircraft built by Boeing was the XB-47 which first flew in 1947. This was an experimental aircraft that led to the creation of the famous B-47 and B-52 bombers. A big problem with jet engines at the time was the huge fuel consumption they had, but with the help of Boeing’s wind tunnel, the largest at the time, it was possible to overcome this issue. Thus, in 1947 the Boeing B-47 Stratojet had its first flight. It had 6 jet engines and was a high-altitude, long-range strategic bomber aircraft.
Boeing in 1950s
The 1950s for Boeing were about producing commercial jet aircraft, developing technology to create new products and building military aircraft with unprecedented capabilities.
Boeing B-52 Stratofortress

In April 1952, the Boeing B-52 made its first flight. It represented the mainstay for the United States bomber force. It is a strategic, long-range aircraft with the incredible ability to carry 70,000 pounds of weapons and a range of 8,800 miles without being refueled. Even today, after almost 70 years this aircraft is still in service.
Boeing’s first commercial jet aircraft
In April 1952, after the first flight of the B-52 Stratofortress, Boeing executives decided to take a huge risk and put $16 million (about $168 million today) into developing a commercial jet. As a result, in July 1954 the Boeing 367-80 well known as the Dash 80 had its first flight. This was the first commercial jet plane built by Boeing. Only one prototype of this aircraft was built, but the company’s risk paid off as the plane was the base design for the KC-135 tanker and the Boeing 707.

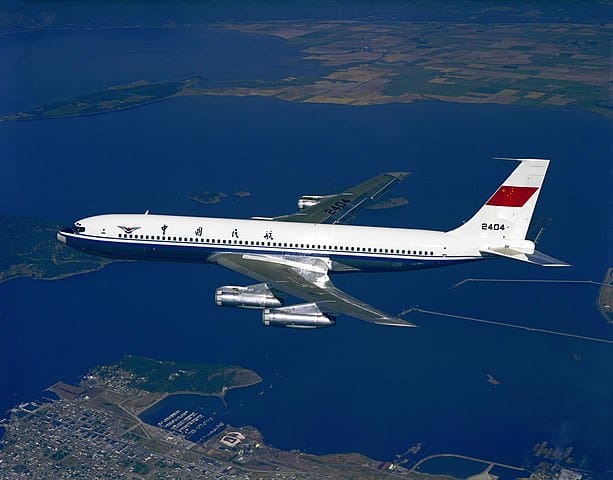
Boeing 707-the first in the famous 7-series

The Boeing 707 was a low-wing, four-engine commercial jet aircraft currently used as a military and charter service plane. It had its first flight in 1957 and was introduced into commercial transport a year later in October 1958 with Pan Am Airways. A total of 800 Boeing 707 aircraft were built between 1956 and 1978. From this aircraft was developed the Boeing 720 (introduced in 1959), a 707 built for shorter routes and able to take off from shorter runways.
Missiles and gas turbine engines built by Boeing
By the 1950s the technology was already quite advanced, and Boeing used it in the company’s attempt to expand its range of operations beyond military aircraft after World War II. Thus, among the new products Boeing created were the short-range missiles used to intercept enemy aircraft. By the time the Cold War got serious, these had been developed into missiles with intercontinental range. Another area where Boeing expanded its operations were gas turbine engines, such as the Boeing T50 and Boeing T60, used for helicopters and ships.
Boeing in 1960s

In the early 1960s, Boeing became a major manufacturer of heavy-lift helicopters after buying Vertol Aircraft Corporation (now Piasecki Helicopter Corporation). This led to the creation of Boeing’s Vertol division (now the Vertical Lift division), which in the 1960s created the twin-rotor CH-47 Chinook and CH-46 Sea Knight helicopters.
On May 21, 1961, Boeing Airplane Co. officially changed its name to The Boeing Company, a name that remains to this day.
Boeing 727- the second aircraft in Boeing’s famous 7 series

In 1960, the Boeing 727 was announced and three years later, on 9 February 1963, it had its first flight. This is the only trijet made by Boeing. The 727 was designed specifically for short flights and smaller airports and it was the first aircraft to exceed 1000 units sold. The plane and its derivatives were produced between 1962 and 1984, resulting in a total of 1832 airplanes. Currently, the Boeing 727 is no longer in commercial use after being retired in 2019.
The Boeing Company’s Involvement in the Space Exploration Age
In 1961, Boeing wins the contract to create the S-IC, the first-stage booster of the American Saturn V rocket used in the Apollo program to explore the Moon.

Two years later, in 1963 Boeing is nominated to create 8 Lunar Orbiter spacecraft with the purpose of photographing the moon. In 1966, the first photos of the moon are sent back to Earth from the first Boeing-built Lunar Orbiter.
Boeing hydrofoils

In the 1960s Boeing also developed hydrofoils, the most popular being the USS High Point (PCH-1) and the USS Tucumcari (PGH-2).
Boeing 737-The third in Boeing’s famous 7 series

In April 1967, the Boeing 737 had its first flight and a year later it was introduced with Lufthansa. It came to complement the Boeing 727’s service on short-haul routes. This twin-engine became the best-selling aircraft of all time in 1987 and maintains this position to this day. Over the years, multiple variants of the 737 have been created, the most recent being the Boeing 737 MAX, introduced in 2017.
Boeing 747-the largest airplane of its time

In the mid-1960s, air travel was increasingly used and the airports were getting more and more crowded. As a result of market demand, in 1966 Boeing announced it would build the world’s largest airplane, with a capacity of 490 passengers. To build such an aircraft, Boeing needed a huge factory, so the largest factory of that time was built in Everett, Washington. Just two and a half years after the program was announced, the first Boeing 747-100 is rolled out in front of the public and the team that made it happen became known as “The Incredibles”. Five months after that, the Boeing 747 Jumbo Jet had its first flight, on 9 February 1969.
Boeing in 1970s
In the early 1970s Boeing was in serious financial trouble. It was hit by multiple events such as the reduction of the US Army’s spending budget for the Vietnam War, the $2 billion debt Boeing made to develop the Boeing 747 project, and the end of the Apollo space campaign in which Boeing was heavily involved. The workers at Boeing’s Seattle plant have suffered the most from this crisis. In just one year, the workforce here went from 80,400 employees to 37,200.
However, the company has pinned all its hopes on the new Boeing 747 jumbo jet, which in 1971 had its first commercial flight, from New York to London with Pan American World Airways. This aircraft completely changed the face of air travel, bringing a plus in passenger comfort, more seats and in the following years became popular worldwide under the nickname “Queen of the Skies”.
Boeing 2707-Boeing’s supersonic passenger airliner

The Boeing 2707 was a project for the first American supersonic transport plane (SST), but it never reached the market. At the end of 1966, the federal government chose Boeing to create an aircraft that would be a direct competitor to the French-English supersonic airliner Concorde. The B2707 was intended to be bigger and faster than the well-known Concorde, but this involved huge costs.
After years of funding, the US government decides that the costs increased too much and stopped funding the project in 1971 before the prototype is even completed. This was another significant event that adds to the series of events that brought a major financial crisis in the Boeing Company in the early 1970s.
Major achievements of Boeing in the 1970s
- Boeing wanted to expand its operations beyond military, civil aviation, and space exploration involvement, thus Boeing Computer Services (BCS) was born in 1970. It was built to support various internal operations within the company but grew so that by 1973 BCS had sales offices to support various commercial computer products (e.g. time-sharing computer service).

- Boeing built the U.S. Standard Light Rail Vehicle (SLRV), a light rail vehicle that was used in San Francisco and Morgantown. This project was developed by Boeing Vertol and a total of 275 such vehicles were built between 1976 and 1979.

- In 1974, NASA buys a B747 aircraft and asks Boeing to modify it to carry the space shuttle. Three years later, in 1977 the first Space Shuttle Carrier aircraft is delivered and ready to enter service.
- The Boeing E-4, a military command and control aircraft, was also created from a Boeing 747. It was introduced in 1974 and a total of 4 units were built.
Boeing in the 1980s
In the 1980s Boeing began to recover from the financial crisis it had entered in the previous decade. The Boeing 747 aircraft turned out to be a winning bet for the company, and in December 1980, the 500th Boeing 747 rolled out of the Boeing factory in Evertt, Washington. Just 3 years later, another Boeing airplane was proving its supremacy in the airliner industry with the Boeing 737 reaching 1000 units built in 1983.
The introduction of the Boeing 767 and Boeing 757 aircraft
In the late 1970s-early 1980s, the US economy began to grow significantly and with it, the popularity of domestic commercial flights. Boeing stunned the aviation industry by announcing it would produce not one but two new airliners, the Boeing 757 and Boeing 767. They were designed to be more fuel efficient and had features so similar that a pilot who was qualified on one of the two planes could fly both of them.

In September 1981, the Boeing 767 had its first flight and a year later in 1982, it was introduced with United Airlines. The 767-200, the first of the 767 series is a wide-body twin-engine aircraft with a capacity of over 170 passengers. Four more 767s were derived from this aircraft: the 767-200ER, 767-300, 767-300ER, and 767-400ER.

In February 1982, the Boeing 757 had its first flight and entered service in 1983 with Eastern Air Lines. This Narrow-Body twin jet was originally called the 7N7 and was created as a successor to the Boeing 727. It is still in service and the aircraft type has been expanded into 4 types of 757 over the years. From a 757 was created the Boeing C-32, a US military aircraft introduced in 1998.
Boeing’s military and space implications in the 1980s
Following Boeing’s rocket experience and involvement in the Apollo program, it became the number 1 contractor for the International Space Station program. Therefore in 1987, Boeing was awarded a 10-year contract to design the living and working quarters of the space station.
Throughout the 80s, Boeing’s involvement in the military has also been on a high level:

- ÃŽn 1989, the B-2 Spirit stealth bomber made its first flight. This aircraft was built by Boeing and Northrop, with Northrop being the prime contractor on the project.

- The Avenger air defence system and new short-range missiles went into production.

- In 1989, the Bell Boeing V-22 Osprey tiltrotor military aircraft made its first flight, a project Boeing and Bell Helicopter worked on together.
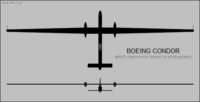
- In 1988, the Boeing Condor had its first flight. It was a fully robotic, ground-controlled aerial reconnaissance aircraft. Only 2 such aircraft were built but unfortunately no customer was found to buy them.
Boeing in the 1990s
By the 1990s, Boeing was already competing with European aircraft manufacturing giant Airbus, so the company’s involvement in creating better-performing aircraft, both civil and military, was greater than ever. Also during this decade, the biggest corporate change in the company occurred when Boeing merged with McDonnell Douglas Corp, a move that brought much criticism against Boeing over the years.
Boeing’s military and space implications in the 1990s

In the early 1990s, the United States Air Force wanted to build a new generation of air superiority fighters, so Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and General Dynamics worked together to create it. Thus was born the YF-22 prototype aircraft from which the F-22 Raptor fighter would be developed. Northrop and McDonnell Douglas also competed for the US Air Force contract, but their YF-23 prototype proved inferior.
In 1993, NASA selected Boeing as the prime contractor for the International Space Station program, and two years later the two parties signed a $5.63 billion contract. During these years, Boeing’s Defense, Space & Security division built Sea Launch to send commercial satellites into space, as well as the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) booster, an unpiloted, upper-stage booster rocket.
Boeing 777-the first airliner to be 100% digitally designed

In June 1994, Boeing 777, the world’s largest twinjet, made its maiden flight and a year later entered service with United Airlines. It was built as a bridge between the Boeing 767 and Boeing 747, having a capacity of 301 to 368 passengers. Its design, created specifically for the requirements of the airlines at the time, was completely digital, using 3D computer graphics software which eliminated the huge cost of creating a full-size mockup. By October 2022, the Boeing 777 series including the 777-200,-200ER,-200LR,-300,-300ER, and B777F have exceeded 1600 units delivered.
The B777 was also the first airliner built by Boeing with the fly-by-wire system, in response to Airbus-built airliners that already had this system implemented.
The development of modern variants for the Boeing 737

In the mid-1990s Boeing decided it was time to develop the Boeing 737 Classic series (-300, -400, -500) and create new, more modern aircraft from it, especially for domestic routes. Thus was born the Boeing 737 Next Generation, which includes the 737-600, -700, -800, and -900 variants. As a result, the first aircraft in the Boeing 737 NG series, the 737-700 flew for the first time in February 1997. This new variant of the Boeing 737 came with a longer wingspan, longer range, and was much more fuel efficient. The 737 Next Generation became the fastest-selling airliner, surpassing even the 737 Classic, with more than 7,000 units sold by October 2022.
Boeing merges with McDonnell Douglas Corp.
In late 1996, Boeing acquires Rockwell aerospace and defense units, which are renamed Boeing North American and will operate as a division of the parent company Boeing. A few months later, on August 1, 1997, Boeing merged with McDonnell Douglas Corp. This huge change in the company brought much criticism, especially after the Boeing 737 MAX crashes, the company being accused of putting its own interests above the lives of the passengers. The merger of the two companies brought together workers with different perspectives, journalist Natasha Frost said that the resulting giant of the two companies took only the name from Boeing and the strategy and work ethic from McDonnell Douglas.

Following this merger, Boeing announces that the MD-95 jetliner aircraft will be added to the famous 7 series as the 717-200.
Boeing between 2000-2022
In 2000, Boeing acquires two more large companies: Hughes‘ space and communications business for $3.75 billion and Jeppesen Sanderson Inc. (the world’s largest provider of flight information services) for $1.5 billion.


In the same year, the Boeing X-32A JSF, an experimental military aircraft made its first flight. Unfortunately, it failed to win the contract with the US Department of Defense over Lockheed Martin’s X-35 aircraft, which would develop into the Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II. Although this loss came as a major disappointment to Boeing, many of the X-32 prototype’s features will be implemented on Boeing’s F/A-18E and -18F Super Hornet aircraft, as well as on other future projects.


In 2001, Boeing succeeds in delivering two large military aircraft, the first Boeing C-40 Clipper was delivered to the US Navy, and the first of four C-17 Globemaster IIIs to the United Kingdom Royal Air Force.
Boeing planes were hijacked in the 9/11 attacks
On 11 September 2001, four flights operated by Boeing planes were hijacked as part of the well-known 9/11 attacks. The first of these, a Boeing 767-200 operating American Airlines Flight 11, crashed into a World Trade Center building. United Airlines Flight 175 also using a Boeing 767-200 crashed into a second World Trade Center building shortly after the first terrorist attack. The other two planes, both Boeing 757-200s operating American Airlines Flight 77 and United Airlines Flight 93 were crashed into the Pentagon and in a rural area of Pennsylvania.
After the 9/11 attacks, Boeing and Siemens Corp. receive a contract from the U.S. Department of Transportation to install explosives detection technology at more than 400 airports in the United States.
Boeing’s most important events in the 2000s
- In September 2001, Boeing begins work to move its headquarters office from Seattle to Chicago.
- In 2002, Boeing merged its defense, space, government, intelligence, and communications operations into a single unit headquartered in St. Louis, Missouri under the name Integrated Defense Systems which would later become Boeing Defense, Space & Security.
- In 2003, the company introduced a new service, Connexion by Boeing, a satellite service that promised passengers access to the Internet. However, other similar services came on the market that were cheaper, and Boeing was forced to discontinue the project in 2006.
- In May 2005, the Boeing KC-767, a military aerial refueling and transport plane had its first flight. It was developed from the Boeing 767-200 aircraft.
- In 2007, the first Boeing 787 Dreamliner rolls out of the factory in Everett, Washington in front of a huge audience.
Boeing 787 Dreamliner

In 2003, at the Paris Air Show, Boeing announces that it will launch a new -7 series airliner, the Boeing 7E7 which will be named the Boeing 787 Dreamliner in January 2005. The first flight of a 787 Dreamliner took place on 15 December 2009 and the aircraft was introduced into service two years later in October 2011 with All Nippon Airways (ANA).
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner aircraft holds the record set in 2008 for the most initial sales since launch in history, that year Boeing reached 857 orders for the 787. The aircraft comes in 3 variants (B787-8, -9,-10) with a capacity of 242 to 310 passengers in a typical three-class configuration. The first two variants, Boeing 787-8 and 787-9 are also sold as business jets by Boeing Business Jet under the name BBJ 787.
Boeing 737 MAX
In 2011 Boeing saw itself losing ground to Airbus, which had just launched the much more fuel-efficient A320neo. So the idea of building a new plane was born, a rebuilt Boeing 737 that was expected to be 5% more fuel efficient than its direct competitor Airbus A320neo.

On August 30, 2011, Boeing introduces the Boeing 737MAX, an airplane designed to be the most fuel-efficient single-aisle airplane on the market. It had its first flight in January 2016 and was introduced into service in May 2017 with Malindo Air. Currently, there are 4 variants of the aircraft, the 737 MAX 7, -8,-9, and -10 which is expected to be delivered for the first time in 2023.
From March 2019 to December 2020, all Boeing 737MAX aircraft were grounded following two similar crashes in which 346 people died: Lion Air Flight 610 and Ethiopian Airlines Flight 302. Following analysis, huge problems were found, particularly with the aircraft’s MCAS system which relied on a single sensor, an unacceptable situation in aviation. Other problems were also found at other levels in the company that was prioritizing profits and finances over passenger safety. Following the correction of the errors found and after multiple tests, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) decides to lift the restrictions and recertify the Boeing 737MAX aircraft in 2020. Boeing has been heavily penalized following the incidents with a total amount of $2.5 billion.
Boeing’s future resolutions
Boeing’s history is a long one, full of events that have changed the course of aviation as we see it today, with powerful implications in military aviation, space exploration, and especially in civil aviation. Today Boeing is known worldwide, and together with Airbus, its European competitor, they have taken over the entire large airliner market.
As for the company’s future, in 2017 Boeing bought Aurora Flight Sciences to focus on exploring electric-powered airplanes. The Boeing company also has a plan to eventually replace all the features of old planes with new technologies, where electric systems will have priority over hydraulic ones and the airplanes’ fuel consumption to be more efficient than ever.